The framework was designed to be practical and can easily be understood by waste disposal site managers or other practitioners who do not have in-depth understanding of all sustainability issues.
What it is... and why
The EcoSWaD model attempts to unite all varoius fields of study alomg with their varrying interpretations and measurements in the context-specific area of sustainability to facilitate a comprehensive and meaningful assessment of waste disposal sites. The framework was designed to be practical and can easily be understood by waste disposal site managers or other practitioners who do not have in-depth understanding of all sustainability dynamics. Also, it is important that the framework is easy to use with available or easily measurable data, especially in developing countries. Furthermore,the framework can be easily applied to a range of WDS situations through simple adaptations for the local socioeconomic, legislative and environmental contexts. The framework can easily identify the critical areas of concerns for improvement to effectiveky manage waste disposal sites.
Site sustainability
In line with the requirement for ecosystem conservation, ecological sustainability of WDS can be defined by the ability of a WDS to take up waste without compromising the health of the surrounding ecosystem, ability of the ecosystem to renew itself nor ability to provide ecosystem services.
Several questions may need to be answered for a site to be considered sustainable:
- What is the sustainability of WDS sites to accept waste over their designed life?
- How will WDS impact on ecosystem health as indicated by the chemical, physical and biological qualities and resilience as indicated by the regenerative capacity and the ecosystems service delivery in the vicinity of WDS?
- How will WDS impact on the environment and cope with the need for more disposal due to increasing waste generation caused by economic development and the role played by WDS in providing livelihoods to local communities?
- How the sustainability of waste disposal sites, especially their ability to fulfil all the above criteria for their designed life span?
Under the hood
In the EcoSWaD framework, there are 35 indicators of the ecological sustainability of WDS which are divided into five major themes, namely: the location sustainability, operational sustainability, environmental sustainability, social sustainability and site capacity. Each indicator has variables which are weighted according to its influence on an indicator with highly influencing variable is give a higher weight value. The maximum weight for variables per indicator is one.
The EVIAVE methodology for making environmental diagnosis of landfills was used as a base for the EcoSWaD framework. The general context of the ‘Circles of Sustainability’ methodology was also used for graphical representation of the data but adapted to represent the five themes for WDS sustainability. By using this context of graphically representing sustainability data, the complexity and diversity of waste disposal sites is simplified, and the interpretations are made easier. Additionally, the challenge of requiring large statistical data or the risk of using narrow one-off surveys for assessing WDS sustainability are reduced. A polygon of sustainability of WDS is generated in the EcoSWaD. Different colours are used to show the classification level of the individual indicators within the themes as illustrated below:
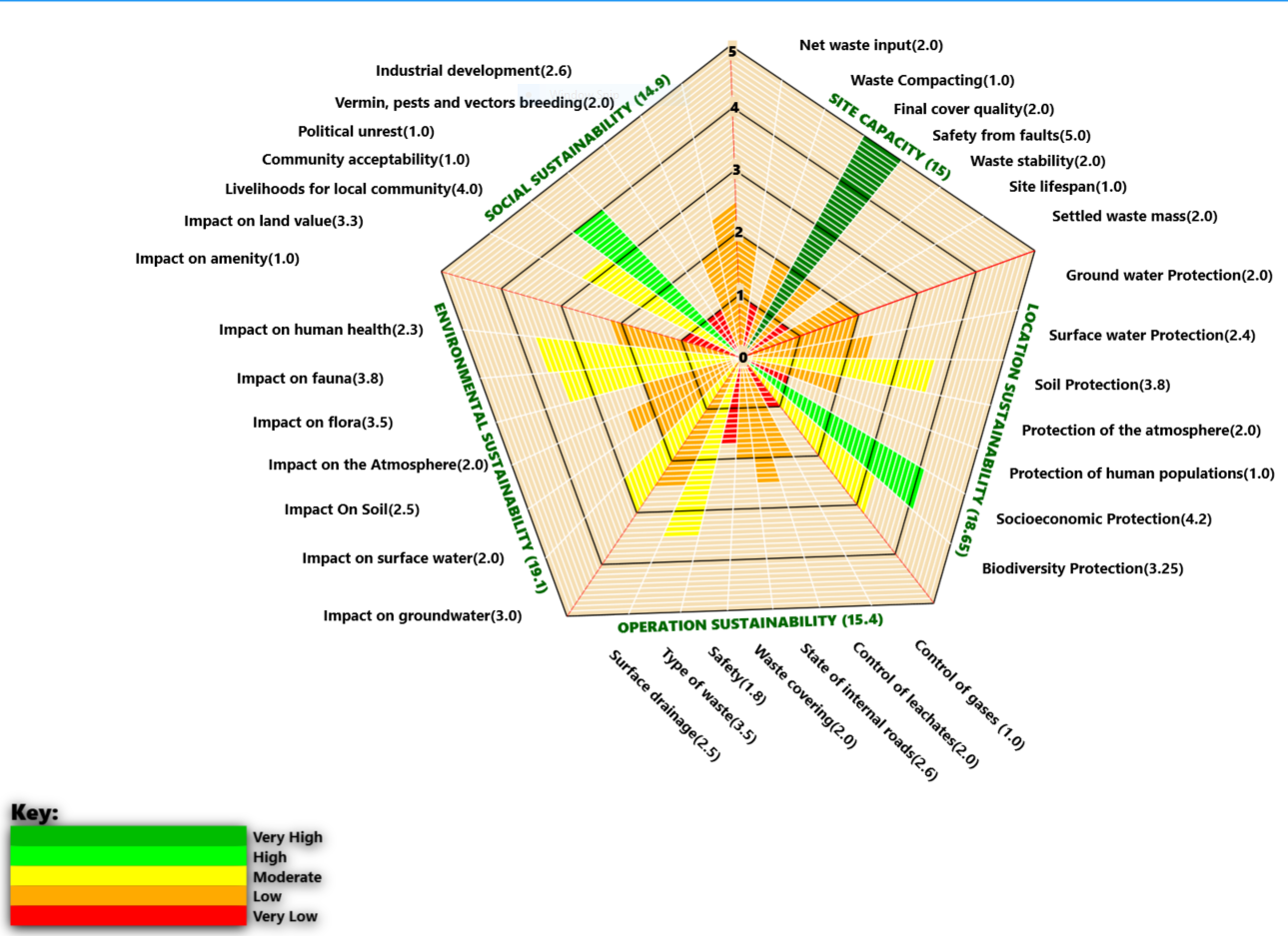
Each variable in the model is assigned a classification value which depends on its condition at the site. The classification values range from 1 to 5 with the least desirable conditions having the lowest values and the most desirable conditions having the highest values (Table 1).
Table 1: Classification of variable and indicator values.
| Classification | Variable value(Vv) | Indicator value(Vi) |
|---|---|---|
| Very Low | 1≤ Vv <2 | 1≤ Vi <2 |
| Low | 2≤ Vv <3 | 2≤ Vi <3 |
| Moderate | 3≤ Vv <4 | 3≤ Vi <5 |
| High | 4≤ Vv <5 | 4≤ Vi <5 |
| Very High | 5 | 5 |
The value of each theme is then obtained from the total of the indicator values within the theme.The maximum indicator value is 35 and lowest value is 7. Table 2 shows the classification of theme values.
The site is then assigned an overall Sustainability Score.The maximum sustainability score value is 175 where each theme is at the maximum value of 35 and the lowest score is 35 where each theme received the lowest value of 7 (Table 2).
Table 2: Classification of theme values and Sustainability Score.
| Sustainability level | Theme value(Tv) | Sustainability Score(Ss) |
|---|---|---|
| Very Low | 7 ≥ Tv <14 | 35 ≥ Ss ≤63 |
| Low | 14≥ Tv <21 | 63> Ss ≤ |
| Moderate | 21> Tv ≤28 | 91> Ss ≤119 |
| High | 28> Tv ≤35 | 119> Ss ≤147 |
| Very High | 35 | 147> Ss ≤175 |
Figure 2 shows the hierarchy of the indexes described above.
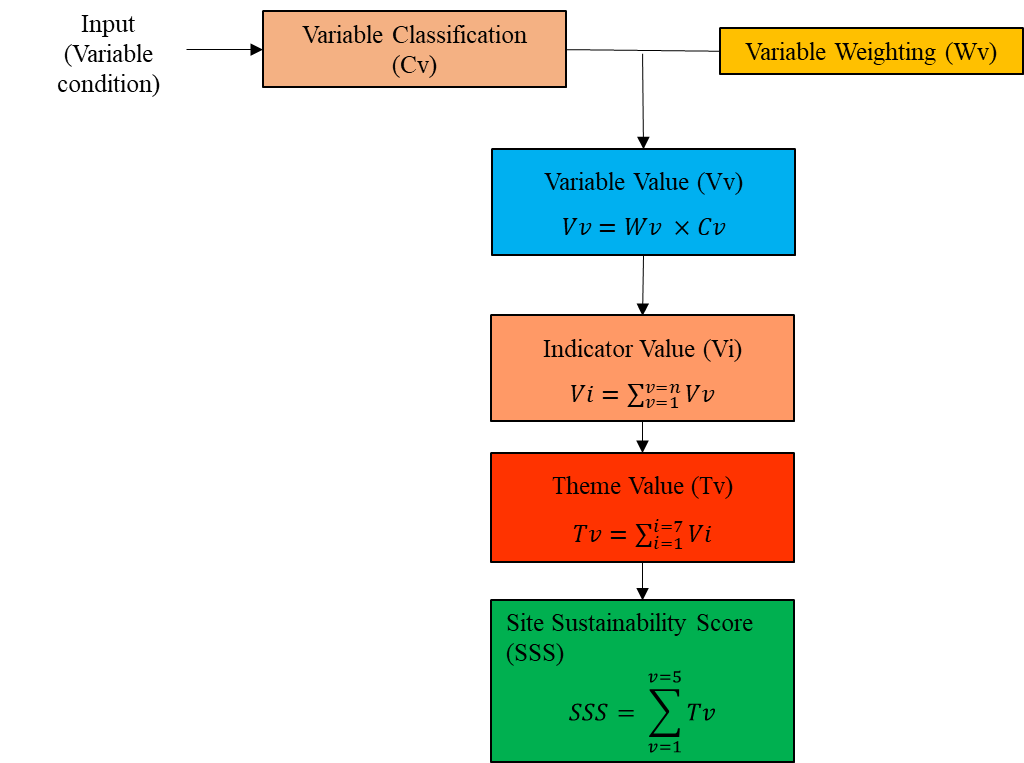
Figure 2: Hierarchy of indexes in the EcoSWaD.
The Themes
-
Location suitability: This theme shows the sustainability of the WDS with emphasis on its location; is the location suitable for protection of environment, community health and property? It answers questions concerning the suitability of site location for minimizing the impact on environmental resources. It also shows which resources are at most risk of being adversely impacted by the location of the site.
It comprises the following indicators:
- Ground water protection
- Surface water protection
- Ground water protection
- Soil protection
- Atmosphere protection
- Human protection
- Social-Economic protection
-
Operational sustainability: This theme assesses if the site operation is suitable for protection of the environmental and community health while focusing on the activities of running the site. The theme can highlight the operational activities causing the most concern at a site and hence need to be improved urgently. This theme also includes all elements of the site design.
It comprises the following indicators:
- Control of gases
- Control of leachate
- State of internal roads
- Waste covering
- Personnel Safety and security
- Waste type
- Surface drainage
-
Environmental sustainability: This theme highlights the site’s current impact on the surrounding environment. It indicates whether the site operation or location is having significant impact on the environment. It shows the extent of the impact on the different environmental components highlighting the most affected components. From this theme, site management can identify which environmental component(s) to prioritize in case of limited resources.
It encompases the following indicators:
- Impact on groundwater
- Impact on surface water
- Impact on soil
- Impact on the atmosphere
- Impact on flora
- Impact on fauna
- Impact on community health
-
Socioeconomic sustainability: This theme shows the site’s impact on the local community. It shows how the site is affecting the community that interact with it and/or lives in the vicinity of WDS. From this theme, the negative and positive effects of the site on the economic and social aspects of the community are highlighted.
Its indicators include:
- Impact on amenity
- Impact on land value
- Livelihoods for local community
- Community acceptability
- Political unrest
- Vermin, pests and vectors breeding
- Industrial development
-
Site capacity sustainability: This theme shows if the current state of the site operation and management allows it to function to its full life span. It shows how the WDS operation impacts on its design capacity to handle waste load, i.e., how the WDS operation and management will contribute to unnecessary exhaustion of the site capacity before its designed life span. The theme gives an indication of whether the site capacity is likely to be exhausted before the projected lifespan of the site.
Its indicators include:
- Net waste input
- Waste Compacting
- Final cover quality
- Safety from ground faults
- Waste stability
- Site lifespan
- Settled waste mass